APA Classes

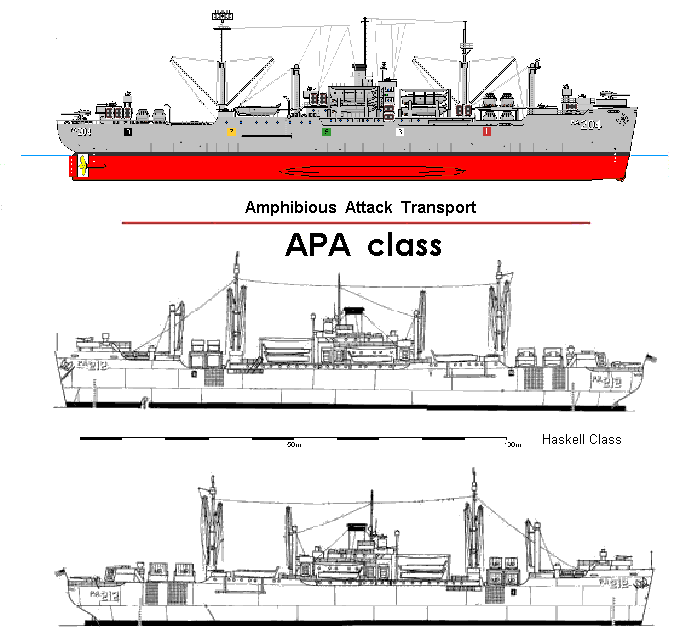
Amphibious Attack Transports
A ship class is a group of ships of a similar design.
A naval ship is a military ship, differentiated from civilian ships by construction and purpose. Generally, naval ships are damage-resilient and armed with weapon systems, though armament on troop transports is light or non-existent. Naval ships designed primarily for naval warfare are termed warships, as opposed to support or "auxiliary" ships.
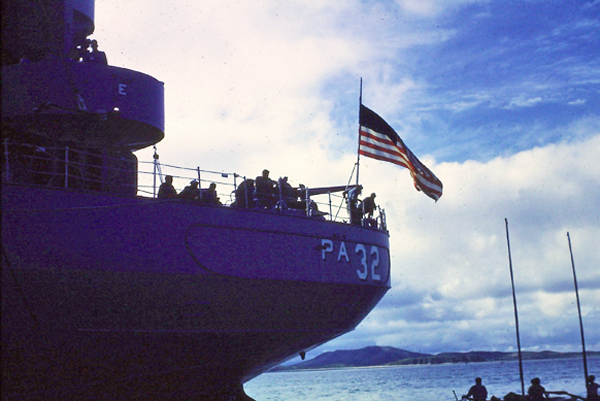
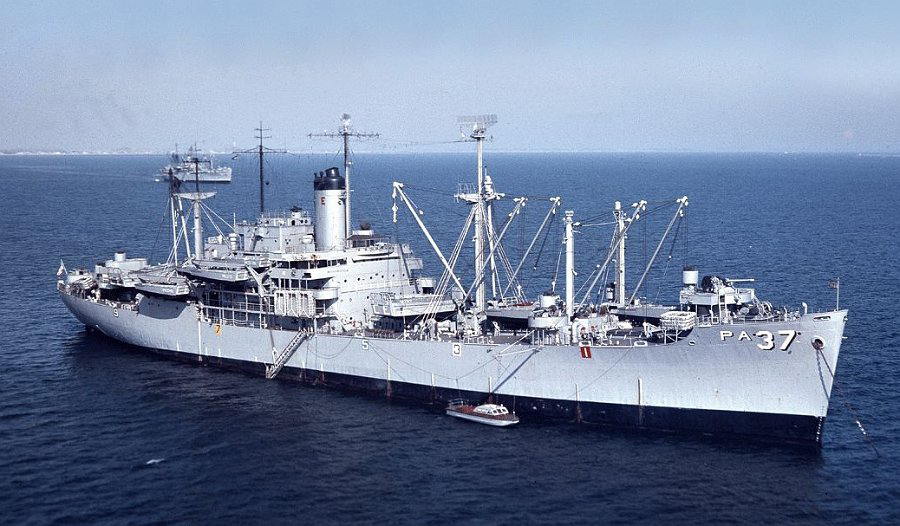
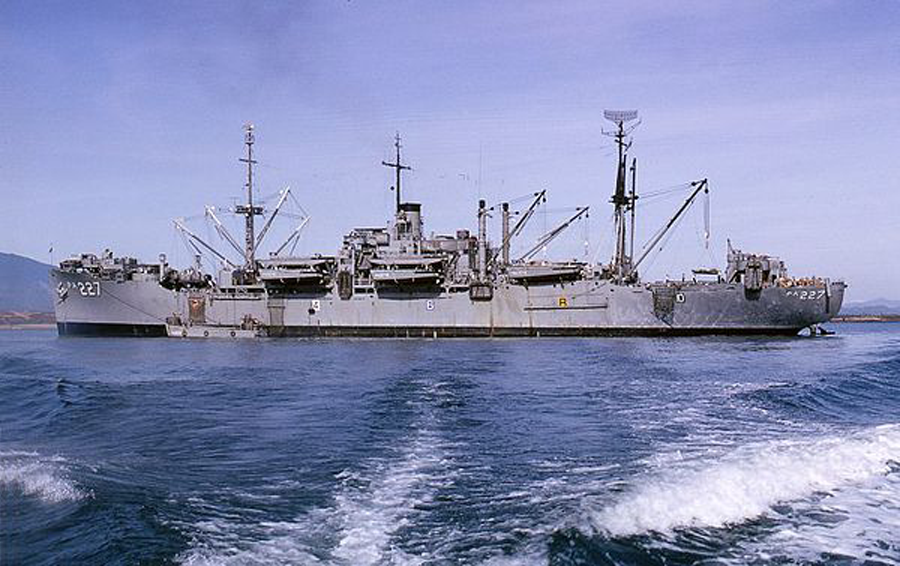
Amphibious/Attack Transports were designed to sail to the site of amphibious operations carrying assault troops and support equipment. APAs had the capacity to hold a full battalion of troops. The APA disembarked troops with the ships own landing craft. The APA would then stand off the beachhead ready to evacuate troops, casualties, and prisoners of war. In order to carry out its primary mission APAs had to provide all facilities for the embarked troops including, berthing, messing, medical and dental care, and recreational facilities. All APAs in the Navy inventory on 1 January 1969 were redesignated as Amphibious Transports or "LPAs".
A total of 388 APA (troop) and AKA (cargo) attack transports were built for service in World War II in at least fifteen classes. Depending on class they were armed with one or two 5-inch guns and a variety of 40mm and 20mm anti-aircraft weapons.
Listed below are 17 classes comprising 248 ships in total.
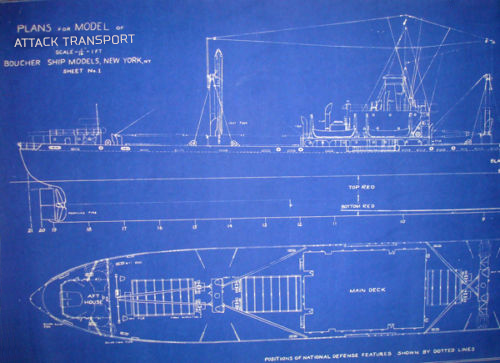
A ship class is a pattern for construction, where the ships of a given class are essentially identical. The lead ship in a class provides the name for that class. Thus, the first ship in the Bayfield-class was USS Bayfield (APA-33).
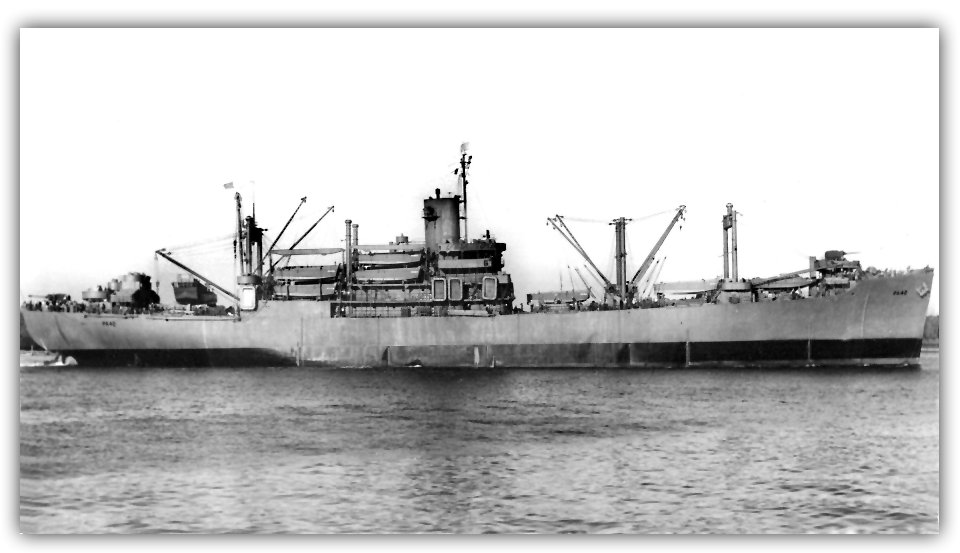

USS Elmore (APA-42), a Bayfield-class APA.

Ship Class
Lead Ship in Class
Commission date of lead ship
Specifications